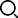What are the potential factors affecting laser cutting machines?
Release time:
2024-06-12
There are three power zones of the laser cutting machine. Understanding them will be of great help in mastering the operation of the laser cutting machine. Let me take you through them.

There are three power zones of the laser cutting machine. Understanding them will be of great help in mastering the operation of the laser cutting machine. Let me take you through them.
Three areas of laser power (overburned area, defect-free area, and slag hanging area)
1. Overburning zone: When the laser power is too high, the heat input is too large, causing the melting range of the workpiece to be larger than the range that can be driven away by the high-pressure airflow. The molten metal fails to be blown away by the airflow and overburning occurs.
2. Defect-free area: that is, the laser power is in a suitable range, and the cutting effect is good at this time, which is called a defect-free area.
3. Slag hanging area: When the laser power is too small and the heat is insufficient, the temperature of the molten product is lower closer to the lower edge, and the viscosity is greater. Therefore, it cannot be blown away by the high-pressure airflow and remains at the lower edge of the cutting surface to produce slag hanging. . In severe cases, incision cannot be made.
Criteria for judging the cutting quality of laser cutting machines
For laser cutting of plates with a thickness of more than 2 mm, the distribution of roughness on the cutting surface is uneven, with large differences along the thickness direction, and its changes have two characteristics:
1. The shape of the cutting surface is divided into two completely different parts. The surface of the upper part is flat and smooth, the cutting stripes are neat and dense, and the roughness value is small; the cutting stripes of the lower part are disordered, the surface is uneven, and the roughness value is large. The upper part is characterized by the direct action of the laser beam, while the lower part is characterized by the erosion of molten metal.
Whether it is continuous laser cutting or pulse laser cutting, the cutting surface displays two parts: upper and lower. The difference is that in pulse laser cutting, the cutting stripes on the upper part have a corresponding relationship with the pulse frequency: the higher the frequency, the finer the stripes and the rougher surface. The higher the value, the smaller the value.
2. The surface roughness in the upper area of the cutting surface is generally uniform and does not change with height; while the surface roughness in the lower area changes with height. The closer to the lower edge, the greater the surface roughness value.
Latest News